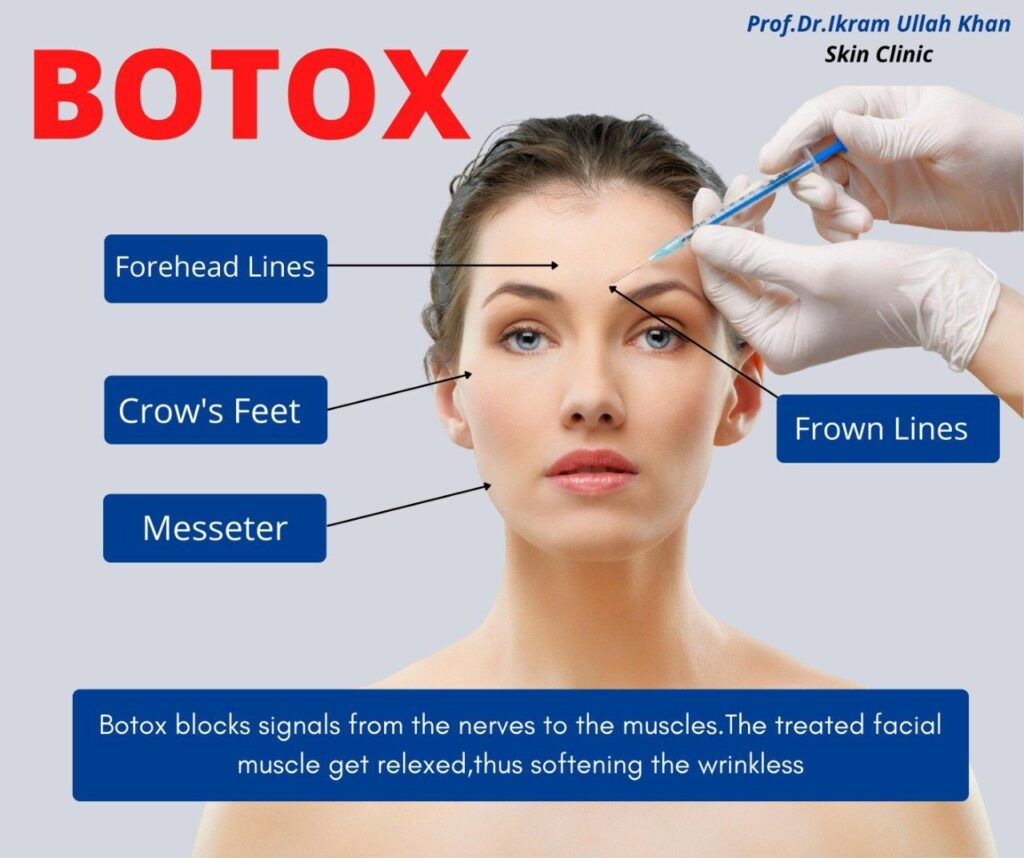
How Botox Works
Botox functions by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that sends signals from nerves to muscles.
When acetylcholine is blocked, the targeted muscle becomes temporarily relaxed.
- In cosmetic use, this relaxation smooths dynamic wrinkles — lines formed by repetitive facial expressions (such as frowning or squinting).
- In medical therapy, muscle relaxation helps relieve spasms, stiffness, or other abnormal muscle contractions.
The effect is reversible. Over time, nerve endings regenerate new connections, restoring normal muscle activity — which explains why Botox results are temporary.
General Duration of Botox Results
On average, Botox lasts between 3 and 6 months.
However, the exact duration depends on several factors, including:
- Treatment area
- Dosage and dilution
- Muscle size and strength
- Metabolism and lifestyle
- Frequency of treatment
Some patients notice their results fade sooner (2–3 months), while others experience effects lasting up to 7–8 months, especially after multiple treatments.
How Long Botox Lasts by Treatment Area
The longevity of Botox varies by injection site because different facial and body muscles differ in strength and activity.
| Treatment Area | Average Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Forehead lines | 3–4 months | Most common treatment; results last shorter in expressive faces. |
| Frown lines (glabellar) | 3–4 months | Deep lines may reappear sooner in highly active muscles. |
| Crow’s feet (around eyes) | 3–4 months | Thinner muscles; duration may vary slightly. |
| Jawline / Masseter muscles | 4–6 months | Larger muscle group; results may last longer. |
| Neck bands (platysma) | 3–5 months | Moderate duration; may need more frequent touch-ups. |
| Underarms (hyperhidrosis) | 6–9 months | Longest-lasting area; sweat glands respond slower to nerve regrowth. |
| Migraines | 10–12 weeks | FDA-approved interval for chronic migraine treatment. |
| Overactive bladder | 6–8 months | Based on clinical studies and medical treatment protocols. |
Why the Duration Differs Between People
Several biological and lifestyle factors influence how long Botox remains effective:
1. Metabolism
People with faster metabolism or higher physical activity tend to break down the toxin sooner, leading to shorter duration.
2. Muscle Strength
Stronger or more active muscles (like the forehead or jawline) regain movement earlier than smaller or less used ones.
3. Dose and Technique
A properly calculated dose and precise injection technique from an experienced professional often result in longer-lasting and balanced effects.
4. Consistency of Treatment
First-time users may experience shorter effects (2–3 months), while consistent use can slightly prolong the duration as the muscles adapt to reduced activity.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, excessive sun exposure, and chronic stress can shorten the duration of Botox effects by affecting skin health and nerve regeneration speed.
When Does Botox Start Working?
Botox does not work immediately.
After injection, the effect gradually begins within 3 to 5 days, and full results are typically visible after 10 to 14 days.
The time to onset may vary based on:
- Area injected
- Dosage
- Muscle size and blood flow
- Individual response
Most clinicians schedule a follow-up visit after two weeks to evaluate results and, if needed, perform minor touch-ups for optimal symmetry.
How to Make Botox Last Longer
While Botox results are temporary, certain habits and care strategies can help you maintain smoother skin or therapeutic benefits for a longer period.
1. Choose an Experienced Injector
The skill and precision of the injector are crucial. A certified and experienced professional understands:
- The correct dosage for each area
- The depth and angle of injection
- How to achieve balanced muscle relaxation
Poor injection technique can lead to uneven results or shorter duration due to incorrect placement or diffusion.
2. Follow Post-Treatment Instructions Carefully
After Botox injections, how you care for your skin can directly affect the outcome.
Do:
- Remain upright for at least 4 hours post-injection.
- Gently move facial muscles (smile, frown, raise eyebrows) for 1 hour to help Botox settle.
- Stay hydrated and maintain healthy skin moisture.
Avoid:
- Rubbing or massaging the treated area for 24–48 hours
- Heavy exercise, saunas, or hot baths for 24 hours
- Alcohol consumption and anti-inflammatory drugs (like ibuprofen) immediately after treatment
These precautions prevent Botox from migrating to unintended areas and help it bind properly at the neuromuscular junction.
3. Maintain a Consistent Treatment Schedule
Regular Botox treatments can “train” muscles to remain relaxed, gradually extending the duration between appointments.
Most dermatologists recommend repeating treatments every:
- 3–4 months for cosmetic use
- 6–9 months for medical conditions (depending on FDA indication)
Skipping treatments for long periods allows muscle activity to return fully, resetting your progress.
4. Protect Your Skin and Overall Health
Healthy skin enhances Botox longevity. Consider these long-term habits:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen daily (UV damage accelerates skin aging).
- Eat a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and hydration.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol, which accelerate toxin metabolism.
- Manage stress levels, as chronic cortisol spikes can influence nerve recovery.
5. Combine Botox with Complementary Treatments
Botox can be combined with:
- Dermal fillers for volume loss
- Laser resurfacing or chemical peels for texture improvement
- Medical-grade skincare (retinoids, peptides) for overall skin health
These combination therapies do not make Botox itself last longer but prolong the appearance of youthful results by improving the underlying skin quality.
Botox Duration in Medical Conditions
While Botox is best known for reducing wrinkles, it is also a powerful therapeutic tool.
Different medical uses have different durations due to varied muscle types and injection depths.
1. Chronic Migraine
- Botox helps reduce migraine frequency and intensity.
- Effects appear after 10–14 days and last about 10–12 weeks.
- FDA recommends retreatment every 12 weeks for consistent relief.
2. Muscle Spasticity
- Used in conditions like cerebral palsy, stroke recovery, and multiple sclerosis.
- Results typically last 3–4 months, depending on muscle tone and severity.
3. Overactive Bladder
- Botox relaxes the bladder muscle, reducing urgency and leakage.
- Results last 6–8 months in most clinical trials.
4. Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating)
- Targets sweat glands under the arms, hands, or feet.
- Lasts 6–9 months, sometimes up to a year in low-sweat individuals.
These therapeutic durations are supported by FDA guidelines and clinical research studies.
Safe Maintenance and Follow-Up
1. Avoid Over-Treatment
Too-frequent Botox injections can lead to antibody formation, where the body becomes resistant to the toxin, reducing its effectiveness.
To prevent this, most practitioners recommend spacing treatments by at least 12 weeks.
2. Monitor for Side Effects
Although generally safe, watch for:
- Localized pain or bruising
- Mild headache
- Temporary eyelid droop (ptosis)
- Uneven smile or facial asymmetry
These effects are usually mild and resolve within days to weeks. Report any severe reactions to your healthcare provider promptly.
3. Reassess Treatment Goals Regularly
Botox should be personalized.
During follow-up appointments, discuss:
- Which areas are responding best
- Whether the dose or technique needs adjustment
- Long-term treatment goals (cosmetic or therapeutic)
A customized approach ensures both safety and maximum longevity of results.
Science, Myths, and Long-Term Outlook of Botox
Botox is one of the most studied neurotoxins in modern medicine. Over the past three decades, it has proven to be both effective and safe when administered correctly.
However, its temporary effect and the variability in duration often lead to confusion and misconceptions.
Let’s explore the science behind its longevity and clarify what’s true and what’s not.
The Science Behind Botox Longevity
After injection, Botox works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction.
When acetylcholine cannot bind to muscle receptors, the muscle remains relaxed.
Over time, nerve terminals regenerate, creating new synaptic connections — this is when movement gradually returns.
Research shows that this regeneration process typically takes 12–16 weeks, which aligns with the average cosmetic Botox duration (3–4 months).
The body naturally metabolizes the Botox protein during this time, meaning the treatment doesn’t remain in your system indefinitely.
Myths vs. Facts About Botox Duration
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Botox can last forever | False. Botox is temporary and always wears off as nerve endings regenerate. |
| More Botox equals longer results | Partly false. Overuse may lead to unnatural stiffness or antibody resistance. The correct dose, not excess, ensures longer duration. |
| If you stop Botox, wrinkles get worse | False. Wrinkles return to their original state; they do not worsen. In some cases, long-term Botox use delays wrinkle deepening. |
| Exercise immediately after Botox helps it work better | False. Intense exercise can cause Botox to migrate, reducing its effectiveness. |
| Botox builds up in the body | False. It is metabolized and eliminated naturally over time. |
Does Botox Last Longer with Repeated Treatments?
Yes, consistent treatments can make results last slightly longer over time.
Here’s why:
- The muscles become “trained” to stay relaxed, requiring less effort to maintain smoothness.
- Repeated treatments may cause mild atrophy (shrinking) of the targeted muscle, which delays wrinkle return.
However, this should always be managed by a licensed professional to maintain natural facial expression and balance.
How Long Should You Wait Between Botox Treatments?
Most experts recommend waiting 3 to 4 months between cosmetic treatments.
Medical Botox treatments (like for migraines or spasticity) may follow specific intervals outlined by the FDA or your specialist (usually every 12 weeks).
Overlapping treatments or excessively short intervals can increase the risk of antibody development — making future Botox sessions less effective.
Long-Term Safety of Botox
Botox has an excellent safety profile when performed by trained professionals.
Long-term studies show no evidence of permanent nerve or muscle damage when used responsibly.
Potential long-term considerations include:
- Mild muscle thinning with repeated injections in the same area (reversible if stopped).
- Temporary resistance if the immune system forms neutralizing antibodies (rare).
Routine medical evaluations and provider communication are key to maintaining both safety and aesthetic goals.
When to Contact Your Doctor
You should promptly consult your doctor if you experience:
- Persistent swelling or redness beyond 48 hours
- Difficulty swallowing, breathing, or speaking (rare allergic reactions)
- Vision changes
- Uneven muscle movement that doesn’t resolve after two weeks
These cases are extremely uncommon but require professional attention.
Key Takeaways
Botox results last 3–6 months, depending on area and individual factors.
Regular treatments can extend longevity slightly.
Post-care and injector skill greatly influence results.
Botox is safe, reversible, and effective when administered properly.
Duration varies between cosmetic (3–4 months) and medical (6–9 months) uses.
FAQ: How Long Does Botox Last?
1. How long does Botox last the first time you get it?
Usually around 2–3 months. As your muscles adapt, later sessions often last closer to 4–6 months.
2. Can Botox results last more than 6 months?
In some individuals — especially with higher doses or larger muscles (like the jawline) — effects can last up to 7–8 months, though this is less common.
3. Does Botox stop working over time?
Rarely. Long-term studies show most patients maintain responsiveness. However, if treatments are too frequent or doses too high, the body may form antibodies that reduce effectiveness.
4. Can I make Botox last longer naturally?
Yes. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking and UV damage, stay hydrated, and get consistent treatments.
5. Is it safe to keep using Botox for years?
Yes. Botox has been used safely for over 30 years in both cosmetic and medical patients.
When properly administered, it does not cause permanent harm or skin damage.
References (for medical accuracy)
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) — Botox (OnabotulinumtoxinA) Label Information
- Mayo Clinic — Botox Injections: Overview and Safety
- American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS) — Patient Safety Guidelines
- American Academy of Neurology — Therapeutic Use of Botulinum Toxin in Neurology
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) — Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin